Genetic testing for malformations involves analyzing a person’s DNA to identify genetic changes that may be responsible for congenital anomalies or birth defects. These malformations can affect various organs and structures, such as the heart, limbs, brain, or facial features. The test helps detect inherited or spontaneous mutations that disrupt normal development during pregnancy. It is especially useful for diagnosing syndromic conditions, understanding the cause of abnormalities, guiding treatment decisions, and assessing recurrence risks for future pregnancies. Genetic testing can be performed using blood, saliva, or tissue samples and is valuable for early diagnosis and personalized medical care.
Choosing genetic testing for malformations provides critical insights into the underlying causes of congenital anomalies, enabling accurate diagnosis and informed medical decisions. It helps distinguish between genetic and environmental factors, guides treatment planning, and allows for early interventions that can improve outcomes. For families, it offers clarity and emotional reassurance by identifying whether a malformation is part of a genetic syndrome or a one-time occurrence. This testing also aids in assessing recurrence risks in future pregnancies, supporting reproductive planning. Overall, it empowers patients, parents, and healthcare providers with precise information for personalized and proactive care.
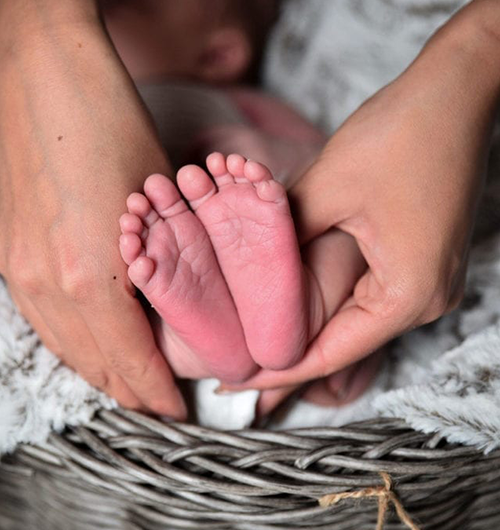
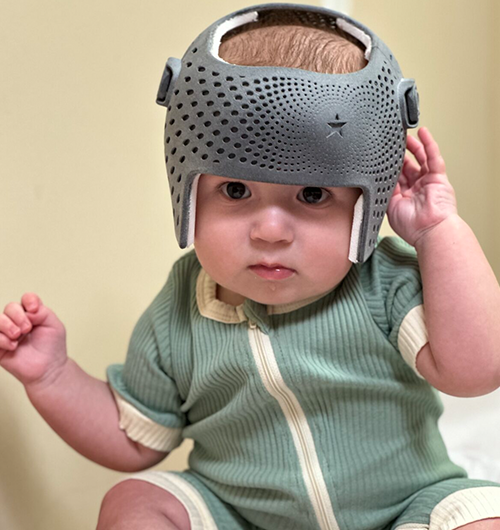
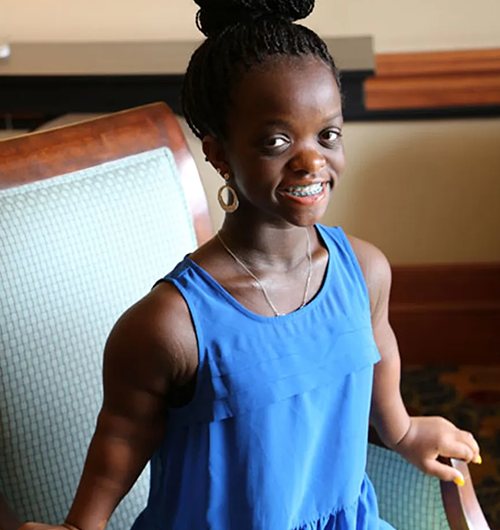


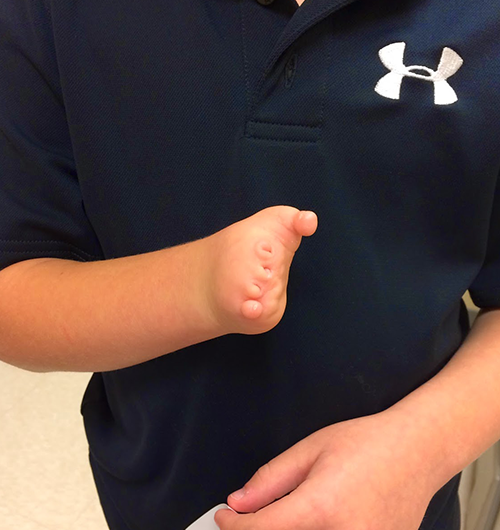


Genetic testing for malformations is recommended for individuals or families facing congenital anomalies or unexplained birth defects. Parents who have had a child with malformations, those with a family history of genetic syndromes, or couples experiencing recurrent miscarriages or stillbirths should consider testing. It is also advised when prenatal scans detect abnormalities or when a child shows developmental delays combined with physical malformations. This testing helps clarify diagnoses, guide medical care, and inform reproductive decisions, providing valuable information for managing current and future pregnancies.
You should consider this test if:

A genetic counselor or healthcare provider explains the test’s purpose, benefits, limitations, and possible outcomes to the patient or parents.
A biological sample is collected, typically blood, saliva, or sometimes tissue, from the individual being tested (or fetus via amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling during pregnancy).
The laboratory isolates DNA from the collected sample for analysis.
The DNA is examined using techniques such as chromosomal microarray, gene panels, or whole-exome sequencing to detect genetic changes linked to malformations.
Geneticists review and interpret the test results to identify mutations or variations that could explain the malformations.
A genetic counselor discusses the results, their implications, and next steps, including treatment options or family planning advice.

 01
01
Our fully integrated E-Lab platform offers online test ordering, real-time tracking, and secure digital reporting bringing convenience and control to both physicians and patients across the country.
 02
02
From routine blood tests to complex genetic panels, we leverage cutting-edge platforms like NGS, PCR, and AI-powered analytics for maximum accuracy and clinical relevance.
 03
03
With lab facilities based in Florida, we ensure faster processing times and direct access to our expert team. You get timely results backed by responsive, local customer support.
At E-lab, we are dedicated to innovation, collaboration, and seamless growth.
